In the fast – paced world of finance, particularly in the broking industry, compliance is more than just a set of legal obligations — it’s a cornerstone of a trustworthy, sustainable, and efficient business. Brokerage firms, whether dealing in stocks, commodities, or derivatives, are subject to a variety of regulatory frameworks designed to ensure transparency, protect investors, and maintain market integrity. In this blog, we’ll explore the key compliance requirements every broking firm needs to follow to stay compliant, secure clients’ trust, and avoid hefty penalties.
What is Compliance in a Broking Firm?
Compliance in a broking firm refers to adhering to a set of laws, regulations, and internal policies designed to ensure that the firm operates within the legal boundaries set by regulatory authorities. This includes ensuring that the firm’s business practices are ethical, transparent, and do not exploit or harm investors.
Failing to meet these compliance requirements can result in severe consequences — including fines, legal action, and damage to the firm’s reputation. Hence, ensuring full compliance is not just about avoiding penalties; it’s about fostering trust, security, and long-term success in the market.
Regulatory Authorities in the Broking Industry
In India, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) is the primary regulatory body for securities markets. In other regions, you’ll find equivalent authorities include :
- U.S.: Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA)
- UK: Financial Conduct Authority (FCA)
- Europe: European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA)
These regulatory authorities set and enforce rules for brokers, ensuring that they comply with the market standards, including capital adequacy, fair trading, and customer protection.
Key Compliance Requirements for a Broking Firm
- Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML)
KYC is one of the most crucial compliance requirements in the financial industry. It involves verifying the identity of clients before establishing a business relationship. Similarly, AML procedures aim to prevent the firm from being used for money laundering or financing of illegal activities.
- Customer Identification Program: Collect details like PAN number, address proof, and a valid ID card.
- AML Monitoring: Continuously monitor transactions to detect and report suspicious activity.
2. Capital Adequacy Norms
A broking firm is required to maintain a certain minimum level of capital, which serves as a cushion against potential market losses. The net worth requirement is mandated by regulatory bodies such as SEBI to ensure brokers can meet their obligations.
- For example, in India, stockbrokers need to maintain a minimum net worth of ₹1 crore (or more, depending on the business model).
3. Client Fund Segregation
One of the fundamental compliance requirements is ensuring that clients’ funds are segregated from the firm’s own funds. This ensures that in case of any financial issues with the broking firm, client assets remain protected and are not used to cover the firm’s liabilities.
- Cash margin segregation is a primary concern to avoid misuse.
- Risk monitoring ensures client funds are always properly safeguarded.
4. Disclosure and Reporting Obligations
Broking firms are required to make regular disclosures to the regulatory authorities, including:
- Quarterly and Annual Audits: Regular financial statements and reports.
- Trade Transparency: Full disclosure of all transactions and trade settlements.
- Customer Communication: Periodic reports to clients regarding their portfolios and trades.
5. Market Conduct and Fair Trading
Brokers must maintain fair market practices, such as avoiding insider trading, market manipulation, or conflict of interest. Any unfair practices could harm investors and undermine market integrity.
- No insider trading: Brokers cannot use non-public information to execute trades.
- Fair commission structures: Brokerages must ensure that their commissions and fees are transparent and reasonable.
6. Suitability and Risk Management
Compliance also extends to ensuring that the products and services offered by the broking firm are suitable for their clients. This includes:
- Risk profiling: Firms must assess each client’s risk appetite before recommending investment strategies or products.
- Suitability checks: Brokers should recommend products only if they align with the client’s investment objectives.
7. Technology and Cybersecurity Compliance
As most broking activities move online, cybersecurity has become a significant part of compliance. Protecting client data and ensuring secure trading platforms is paramount. Regulatory bodies often impose stringent rules on data protection and online trading systems.
- Data Protection: Compliance with GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in the EU, and other data privacy laws.
- Cybersecurity Protocols: Maintaining systems to prevent hacking, fraud, and unauthorized access.
Best Practices for Ensuring Compliance
- Stay Updated: Compliance regulations are dynamic and can change frequently. Regularly monitor updates from regulatory authorities like SEBI or FINRA to stay in the loop.
- Train Employees: Ensure your team is well-versed in the compliance requirements and aware of the consequences of non-compliance. Regular training and internal audits are essential.
- Implement Robust Internal Controls: Maintain clear internal procedures for trade monitoring, client fund management, and transaction reporting.
- Consult Legal Experts: A compliance officer or legal advisor to guide you through complex regulations.
- Use Compliance Technology: Leverage software and tools to streamline the compliance process, from KYC checks to risk monitoring and reporting.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Non-compliance with regulatory requirements can have serious consequences for broking firms:
- Fines and Penalties: Regulatory bodies can impose heavy fines for violations.
- Reputation Damage: Once a firm is found guilty of non-compliance, its reputation may suffer irreparably, affecting customer trust and business.
- Suspension or Revocation of License: In extreme cases, regulators can suspend or revoke the broker’s license to operate, halting all trading activities.
Final Thoughts
Compliance is not just about adhering to legal requirements; it’s about operating with integrity and creating a trustworthy environment for clients and stakeholders. While the regulatory landscape may seem complex, maintaining compliance offers long-term benefits — such as enhanced reputation, client confidence, and operational efficiency.
For broking firms, the key to success lies in staying ahead of regulatory changes, investing in compliance systems, and fostering a company culture rooted in transparency and ethical practices.
Fixed income mutual funds are generally considered a safer than equity funds, but they are not entirely risk-free. They offer a more stable and predictable income stream with lower volatility, making them suitable for conservative investors focused on capital preservation and income generation. However, risks such as interest rate risk, credit risk, and inflation risk can still affect the returns of these funds.
- Lower Volatility:
Fixed income funds invest in bonds and other debt instruments, which tend to be less volatile than stocks. This means the price fluctuations are generally smaller, providing a more stable investment experience.
- Income Generation:
These funds aim to provide regular income to investors through interest payments from the underlying bonds.
- Diversification:
Fixed income funds can help diversify a portfolio by adding a layer of stability and reducing overall risk.
- Interest Rate Risk:
Rising interest rates can negatively impact the value of bonds held by the fund, potentially reducing returns.
- Credit Risk:
There’s always a risk that the issuer of a bond may default on its payments. This risk is higher for bonds with lower credit ratings.
- Inflation Risk:
If inflation rises faster than the interest rate on the bonds, the real return (after accounting for inflation) may be lower or even negative.
- Liquidity Risk:
While many fixed income funds are open-ended and allow for easy redemption, some may have restrictions or penalties for early withdrawals, especially if they invest in less liquid assets.
How Does Inflation Affect Fixed Income?
Inflation typically has a negative effect on the value of fixed-income securities. As interest rates rise, the prices of bonds decline. This is because bond prices and interest rates are inversely related.
Who Fixed Income Investments Are Best for:
Fixed-income securities are recommended for conservative investors seeking a diversified portfolio. The portion of the portfolio allocated to fixed income depends on the investor’s risk tolerance and investment style. For example, an investor may choose to hold a balanced portfolio with 50% fixed-income products and 50% stocks. Example of fixed-income products include treasury bonds and bills, municipal bonds, corporate bonds, and certificates of deposit (CDs).
Share trading can be rewarding—but only if done with smart, disciplined stategies. Many new investors enter into the market expecting quick profits, only to be caught off guard by volatility and losses.
In this blog, we share practical tips to help you invest in the share market wisely and avoid common mistakes.
1. Understand Before You Invest
Before putting your money into any stock, understand the business model, financials, and industry it operates in. Avoid buying shares based on random tips or social media hype.
Smart Tip: Read basic financial statements and track company news regularly.
2. Start Small, Grow Steadily
If you’re new to share trading, begin with a small capital. Learn how the market behaves, how orders are executed, and how prices fluctuate.
Smart Tip: Use virtual trading or paper trading platforms before investing real money.
📊 3. know the Difference Between Trading and Investing
Trading is short-term. Investing is long-term. Each requires different mindset and strategies. Don’t mix the two unless you fully understand the risks.
Smart Tip: Define your goal—quick gains or long-term wealth—and plan accordingly.
4. Diversify Your Portfolio
Don’t put all your money into one stock or sector. Diversification spreads your risk and protects your capital during market downturns.
Smart Tip: A well-balanced portfolio include large-cap, mid-cap, and defensive stocks.
5. Follow a Stop-Loss Strategy
Set a stop-loss to limit your losses in case the trade doesn’t go as expected. This is especially important for intraday and swing traders.
Smart Tip: Never trade without a stop-loss—even if you’re confident.
6. Don’t Let Emotions Drive Decisions
Greed and fear are a trader’s biggest enemies. Be objective, follow data, and avoid emotional decisions, especially in volatile markets.
Smart Tip: Stick to your strategy and avoid panic selling or over-trading.
7. Keep Learning and Adapting
The share market is constantly evolving. Stay updated with financial news, earnings reports, global trends, and technical analysis.
Smart Tip: Read blogs, watch tutorials, and follow SEBI-registered advisors for incredible insights.
8. Choose the Right Broker
A good broker offers more than just a trading platform—they offer research, tools, insights, and support.
Smart Tip: Open your Demat & Trading account with a SEBI-registered, trustworthy broker like Pentad securities.
📌 Conclusion
Success in share trading doesn’t come overnight. It requires patience, discipline, and sound strategy. Follow these smart tips, keep your emotions in check, and treat the market as a place for learning—not gambling.
An IPO, or Initial Public Offering, is when a privately held company offers its shares to the public for the first time, transitioning into a publicly traded company. This process enables the company to raise capital from public investors to fund expansion, pay off debt, or pursue other business objectives. For investors, an IPO provides the first opportunity to buy shares in a company and potentially benefit from its future growth.
Key Features of an IPO
- Private to Public:
An IPO marks the shift from private ownership, with shares made available to general investors through the stock market.
- Raising Capital:
Companies use IPOs to raise significant funds by selling shares to a broader investor base.
- Stock Market Listing:
After an IPO, the company’s shares are listed on a stock exchange, enabling public trading
- Listing Gains:
- Before going public, the company sets an “issues price” for its shares.
- If the IPO is well-received by the market, shares may trade at a higher price on the listing day.
- This difference between the listing price and the issue price is known as a listing gain.
- Investors allotted shares in the IPO can sell them at this higher price to realize immediate profits.
- Long-Term Appreciation:
- If the company performs well post-IPO, its value may increase over time
.
- This can lead to a gradual rise in the share price over time, rewarding long-term investors.
- Holding on to shares of a well-performing company can yield significant returns in the long run
- Other Benefits:
- Access to high-growth companies:
Many IPOs involve business in emerging sectors or with innovative business models, offering strong growth potential.
- Diversification:
IPO investments can diversify an investor’s portfolio by adding exposure to new and potentially dynamic companies.
- Liquidity:
Once listed, the company’s shares are easily tradable on the stock market, providing flexibility to buy or sell.
Important Considerations:
- Risk: IPOs can also be volatile, and there’s no guarantee that share price will rise after listing.
- Market Conditions: Overall market performance of the stock market can impact IPO returns.
- Company Performance: The company’s actual performance post-listing is crucial for long-term investment success.
A Systematic Investment Plan (SIP) is a smart and easy way to invest money in mutual funds regularly. Instead of investing a large sum all at once, you contribute a small, fixed amount every month. This helps you build wealth gradually and steadily over time. SIPs promote disciplined saving and make a consistent habit, with the process happening automatically.
Benefits of SIP
1. Disciplined Saving: A fixed amount is invested every month, regardless of market conditions or personal preferences. This regular habit helps build a strong financial foundation over time
2. Affordable Entry: One of the biggest advantages of SIP (Systematic Investment Plan) is its low entry barrier. You can start investing with as little as ₹500 per month, making it accessible to everyone.
3. Rupee Cost Averaging: SIPs allow you to buy more units when prices are low and fewer when prices are high, helping average out your investment cost over time.
4. Power of Compounding: Compounding means earning returns not just on your original investment but also on the returns generated. Over time, this can significantly grow your wealth
5. Flexible and Convenient: SIPs offer complete flexibility. You can start, stop. Increase or decrease your investment amount at any time, making it easy to adapt to your changing financial situations
Most of us who invest in the stock market aim for good returns with minimal risk. However, the truth is—no investment is entirely risk-free. As Albert Einstein once said, “A ship is always safe at the shore, but that is not what it is built for.” Similarly, higher returns often require a willingness to take on greater risks.
While some risks are manageable, others are beyond our control. The key lies in understanding the types of investment risks and learning how to minimize their impact. Let’s explore the major types of investment risks you may encounter.
What is Investment Risk?
Investment Risk refers to the possibility of losing money or receiving lower-than-expected returns due to changes in the market or in specific investments.
Major Types of Investment Risks
1. Market Risk (Systematic Risk)
Market risk affects the overall financial markets and arises from factors such as economic slowdowns, natural disasters, political instability, interest rate changes, or inflation. This type of risk cannot be eliminated through diversification, as it impacts almost all stocks.
Types of market risk include:
- Equity risk
- Currency risk
- Interest rate risk
2. Specific Risk (Unsystematic Risk)
Specific risk is unique to a particular company or industry, and may arise from factors such as management failures, product recalls, or sector-specific regulations. Unlike market risk, specific risk can be reduced or even eliminated through diversification.
3. Volatility Risk
Volatility refers to the degree of price fluctuation in an investment over a short period. It is commonly observed in derivatives where prices can shift rapidly based on the value of the underlying asset. High volatility increases uncertainty, thereby raising the overall investment risk.
4. Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate risk primarily affects debt instruments like bonds. As interest rates rise, bond prices tend to fall; conversely, when interest rates fall, bond prices rise. Investors can minimize this risk by holding bonds until maturity.
5. Default Risk (Credit Risk)
Default risk refers to the possibility that a borrower may fail to repay interest or principal on a loan or bond. This risk is more common in unsecured instruments. To minimize exposure, Always check the credit rating of a company before investing in its bonds or debentures.
6. Inflation Risk
Inflation risk refers to the loss of purchasing power due to rising prices over time.Fixed-income investments such as bonds, are particularly vulnerable to this risk. As inflation, the real return on your investment may diminish or even become negative.
7. Reinvestment Risk
Reinvestment risk arises when proceeds from an investment such as interest payments or maturity amounts must be reinvested at a lower interest rate. For example, if your bond matures and prevailing interest rates have dropped, your future returns may be lower. One wat to avoid this by using the funds instead of reinvestin them, although that may not align with long-term growth goals.
8. Liquidity Risk
Liquidity risk occurs when you’re unable to sell an asset quickly without significant loss. While stocks and bonds are generally considered liquid, assets like real estate, art, or collectibles may not have ready buyers. In emergencies, investors might be forced to sell such assets at a discounted price.
9. Political or Regulatory Risk
Government policy changes can significantly impact specific industries or the overall economy. Regulatory reforms, change in taxations, or political instability can lead to sharp market movements. In such situations, It’s best to avoid panic selling and intead adopt a ‘wait and watch’ strategy.
Final Thoughts
No investment is completely risk-free. The key lies in understanding the different type of risks, manage them wisely, and investing in line with your personal risk tolerance. While risks are inevitable, the potential rewards of well – informed investing can far outweigh them.
At Pentad Securities Private Limited, a SEBI-registered stockbroking firm since 2012, we blend cutting edge technical tools with expert research to guide our clients toward smarter financial decisions. Open a Demat account with us today and take your first step toward confident. intelligent investing.
For the stock market, repo rate cuts typically lower the cost of capital, encouraging borrowing and investment. This can boost corporate earnings and investor confidence. Rate-sensitive sectors such as banking, real estate, and automobiles often lead the rally, benefiting from cheaper credit and increased consumer demand.
On the corporate front, reduced borrowing costs can tip the scales in favour of greenlighting expansion projects, even as the ongoing tariff war between the US and China continues to disrupt supply chains, increase input costs, and create uncertainty for export-oriented industries. These external shocks affect investor confidence and corporate planning, complicating the RBI’s task of balancing growth and inflation.
When the RBI changes the repo rate, it doesn’t just affect the overnight borrowing cost for financial institutions; it shifts the risk-reward balance across different assets. The immediate impact is seen in the money market, where overnight rates adjust quickly. However, the more significant effect play out over weeks or even months, as banks and non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) reassess lending rates, companies reconsider investment plans, and investors adjust expectations for future earnings.
The stock market can sometimes rise when investors believe that lower borrowing costs will help companies increase their profits. Sectors like banking, real estate, and automotive tend to benefit the most from lower interest rates, leading to potential gains in these stocks. However, if the market had already anticipated the rate cut, the impact might be minimal, or the market could even decline if other negative factors, such as global trade concerns, overshadow the cut.
An increase in money supply due to rate cuts can sometimes weaken the rupee against the dollar. This devaluation may raise concerns among investors, as it could signal economic instability or raising inflation.
A higher repo rate raises the cost of borrowing for companies. When it happens, stock prices often decline as investors become more risk-averse. Conversely, when the repo rate is slashed, sectors such as banking, finance and real estate tend to benefit due to cheaper credit and increased consumer spending.
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), in collaboration with KFin Technologies and CAMS, has launched SEBI MITRA — a centralized initiative designed to help investors locate and reclaim unclaimed or forgotten mutual fund investments.
If you suspect you have idle or unclaimed investments, here’s how to use SEBI MITRA to trace and recover them:
Step-by-Step Guide to Using SEBI MITRA
1. Access the Official Portal
Go to www.mfcentral.com, the official platform designated for SEBI MITRA services.
2. Enter Your PAN
Input your Permanent Account Number (PAN) to begin the search for mutual fund folios linked to your credentials.
3. Verify Your Identity
An OTP (One-Time Password) will be sent to your registered mobile number or email ID. Enter the OTP to proceed securely.
4. Add Additional Details (Optional but Recommended)
To maximize your chances of finding older or inactive folios — especially those created before PAN became mandatory in 2007 — you may also provide:
- Registered mobile number
- Email ID
- Bank account number
- City, PIN code, or full address
- Date of birth or nominee details
These details help in tracing folios that may not be directly linked to your PAN.
5. Start the Search
Click “Proceed” to initiate the search. The system will scan across all participating Asset Management Companies (AMCs) to identify inactive or unclaimed folios linked to your details.
6. Review Results & Update KYC (If Required)
If any folios are found:
- Follow the platform’s instructions to complete or update your KYC (Know Your Customer) formalities
- You can then begin the process to reclaim your identified investments
Important Notes
- A folio is considered inactive if there has been no investor-initiated transaction (financial or non-financial) for 10 consecutive years. These may still hold valuable units or balances.
- Each user is allowed up to 25 search attempts, giving ample scope to refine and explore forgotten assets.
SEBI MITRA is accessible Through:
- MF Central
- Individual Mutual Fund AMCs
- AMFI (Association of Mutual Funds in India)
- SEBI’s official site
Policy Backing
This initiative follows SEBI’s circular dated March 28, 2024 (Ref: SEBI/HO/OIAE/OIAE_IAD-1/P/CIR/2024/XX), aimed at:
- Strengthening investor protection
- Facilitating easy access to unclaimed assets
- Simplifying the recovery process for mutual fund investors
Conclusion
By following these simple steps, you can reconnect with forgotten investments, safeguard your financial legacy, and ensure that your mutual fund holdings are consolidated under your control.
If you’re planning to become an Authorised Person (AP) in the securities market under Pentad Securities, here’s a comprehensive guide to help you understand the process, requirements, and associated fees. This guide covers the documentation checklist, fee structure across exchanges, registration steps, and office requirements.
✅ Checklist for Appointment of Authorised Person (Individual)
Before initiating the registration process, make sure you have the following documents ready:
- PAN Card Copy
- Residential Address Proof
- Educational Proof (Minimum qualification: 10th Pass)
- Bank Proof
📊 AP Registration Details Across Exchanges
| Activity | NSE | BSE | MCX |
|---|---|---|---|
| AP Registration | ₹5,000 + GST per segment | ₹4,000 + GST per segment | ₹2,000 + GST per segment |
| AP Cancellation | Nil | ₹1,000 | ₹2,000 |
| Annual Maintenance Charge (AMC) | ₹5,000 + GST (all segments) | ₹4,000 (all segments) | ₹250 per quarter |
| Processing Fee | ₹500 | ₹500 | ₹500 |
💳 Payment Details for AP Registration & Cancellation
Ensure payments are made to the account below for all NSE-related AP activities:
- Account Title: PENTAD SECURITIES PRIVATE LIMITED – NSE CASH PROPRIETORY ACCOUNT
- Account Number: 200999655681
- IFSC: INDB0000033
📝 Processing Steps for AP Registration
- Draft Agreement – Created based on submitted documents.
- Agreement Execution – Signed on stamp paper after confirmation.
- Uploading – The signed agreement is uploaded to the respective Exchange portal.
- Approval – Upon approval by the Exchange, the AP Code will be issued.
- Intimation – Confirmation and AP code are sent via registered email.
🏢 Requirements in AP Office
To ensure compliance and readiness for operations, the following must be maintained in the AP’s office:
- SEBI Registration Certificate
- Visitor Register
- Complaint Register
- Pentad Securities Name Board
- Recorded Telephone Line (if trading terminals are provided)
- AP Registration Certificate
Becoming an Authorised Person is a crucial step toward building your presence in the capital market ecosystem. Ensure that all documentation and office compliance requirements are strictly adhered to for a smooth and successful registration process.
Open Pen App :
- Tap on icon [ ]at bottom right corner.
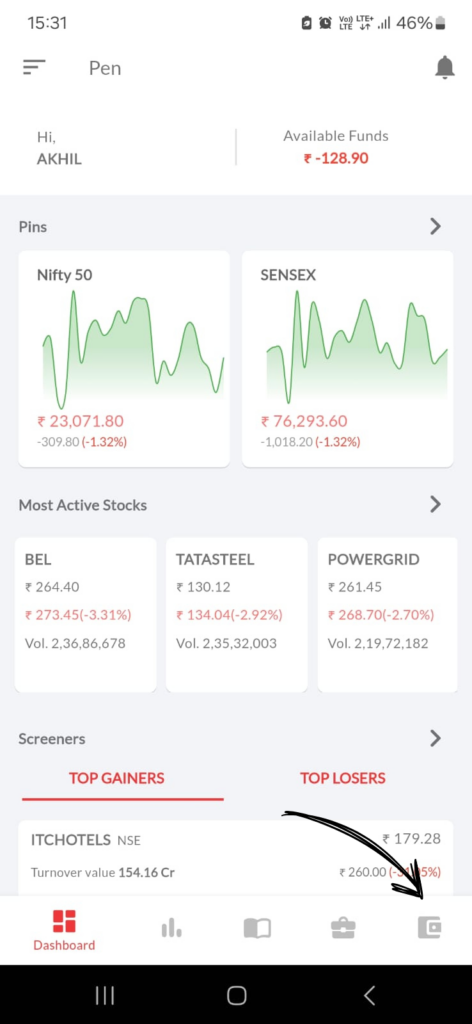
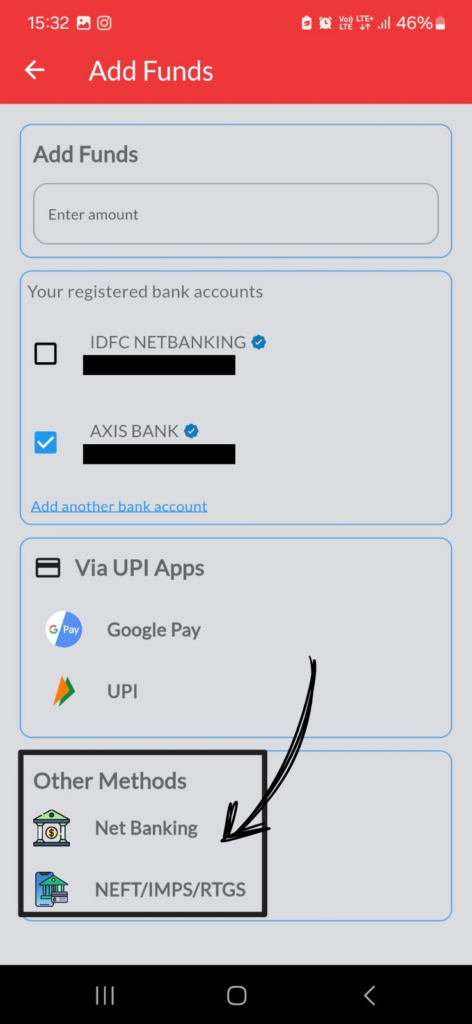
2. Tap on Add Funds
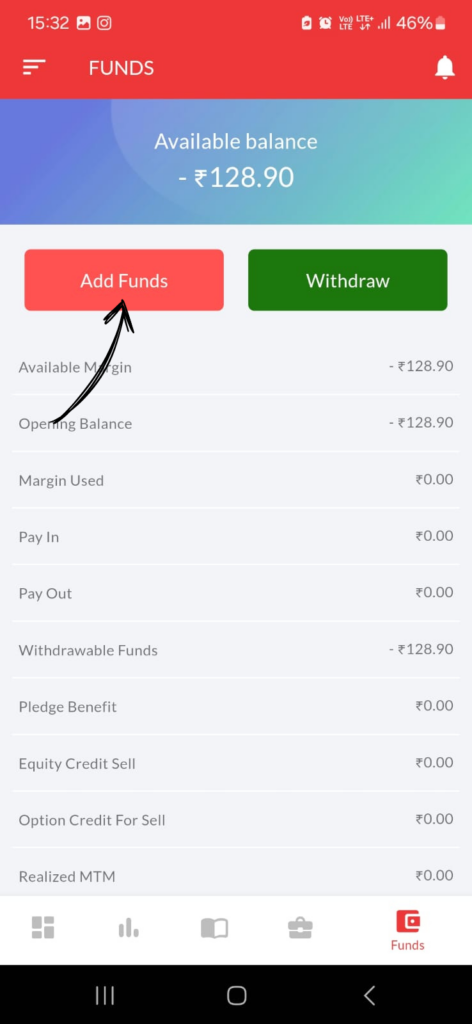
3. Type amount in the blank column.
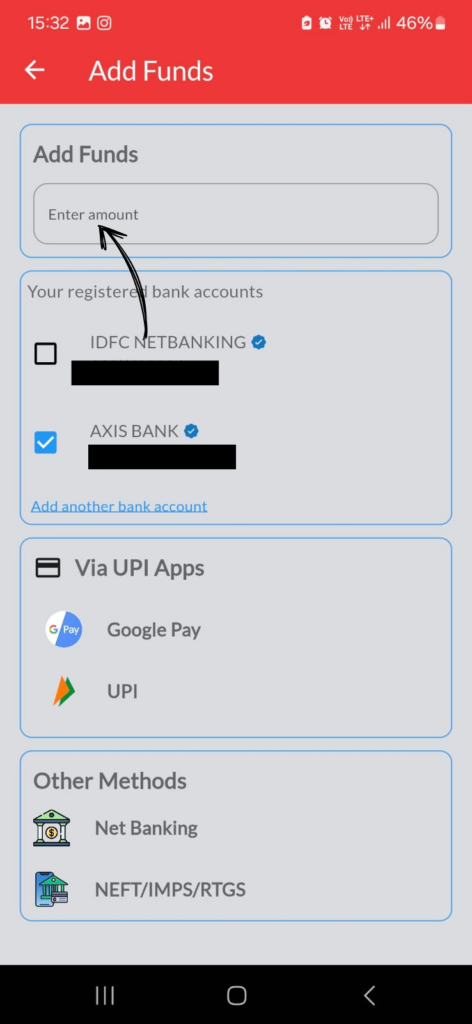
4. Select registered bank A/c, if the client has registered more than 1 bank a/c with us.
5. Select the UPI App whichever is installed in your mobile.
6. It will automatically open the UPI APP.
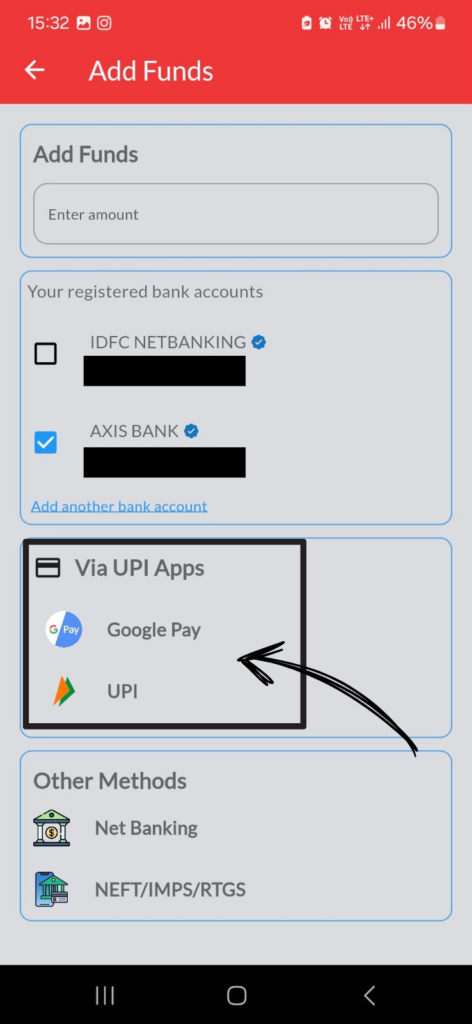
7. In case you have no UPI App in your mobile , you can select net banking option. It will automatically open your registered bank internet banking login page.